AI News – Highlights from November 14–21: Models, GPU Shifts, and Emerging Risks

This week’s AI news highlights major shifts across frontier models, GPU infrastructure, autonomous agents, and global regulation. Readers gain a clear understanding of the technologies shaping 2025 and how they impact developers, researchers, and engineering teams. These updates underscore a deeper tension between accelerating innovation and the operational, security, and governance challenges emerging alongside it.
Find the latest weekly AI news on our main page, updated regularly.
This Week’s Essential AI News at a Glance
Executive Summary
This week brings several high-impact developments in the AI ecosystem. Nvidia reported a record data-center quarter, with demand for its Blackwell GPUs exceeding supply, as covered by The Wall Street Journal (source) and CNN (coverage). Microsoft expanded its strategy with a multibillion-dollar investment in Anthropic, securing up to one gigawatt of compute on Blackwell and Vera Rubin clusters, according to the Microsoft Blog (announcement) and Anthropic’s own statement (details).
Google released Gemini 3 Pro, achieving new benchmark records and delivering a one-million-token context window, as reported on the Google Blog (announcement) and TechCrunch (analysis). Baidu unveiled ERNIE 5.0, a multi-trillion-parameter multimodal model challenging global competitors, according to PR Newswire (release) and China Daily (coverage). OpenAI launched GPT 5.1 Codex Max, focused on long-horizon engineering workflows, with details on the OpenAI Blog (announcement) and additional reporting from VentureBeat (analysis).
DeepMind advanced agentic capabilities with SIMA 2, doubling its predecessor’s performance in 3D environments, as detailed in the DeepMind Blog (release) and covered by MarkTechPost (article). World Labs released Marble, making text-to-3D generation accessible, explained by TechCrunch (report) and expanded by Skywork AI (documentation).
Anthropic disclosed a state-linked cyber-espionage operation that used Claude-based agents to automate up to 90 percent of intrusion workflows. Their official report details the incident (Anthropic report), with additional context from Axios (coverage).
Regulatory shifts accelerated as the US prepared federal action to override state-level rules, according to Axios (report), and the EU introduced the Digital Omnibus package, adjusting GDPR and delaying AI Act obligations, as outlined on the EU Digital Strategy website (proposal) and analyzed by Gibson Dunn (report).
Why This Week Matters
These developments show how AI is evolving on three fronts: expanding compute capacity, new frontier-model capabilities, and more autonomous agents in complex environments. For developers and enterprises, this week’s news influences decisions around model selection, GPU availability, deployment strategies, security posture, and compliance planning. Innovation is accelerating rapidly, while regulation and infrastructure struggle to keep pace.
GPU Infrastructure, Capacity Crunch, and Industry Alliances
Nvidia’s Data-Center Surge and Blackwell Demand
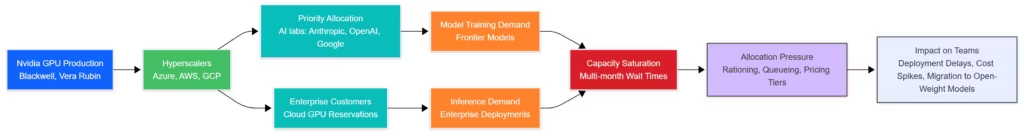
Nvidia’s latest earnings confirm the central role of GPU scalability in the global AI economy. Data-center revenue exceeded expectations, with demand for Blackwell GPUs surpassing near-term supply. Insights from The Wall Street Journal (coverage) and CNN (report) note that hyperscalers face month-long GPU queues and enterprises encounter allocation constraints that directly influence training, inference, and deployment timelines.
Microsoft–Nvidia–Anthropic Partnership
Microsoft and Nvidia strengthened their hardware strategy through a joint investment of roughly 15 billion dollars in Anthropic. This collaboration is outlined in the Microsoft Blog (announcement) and expanded upon in Anthropic’s Foundry integration post (details). The agreement enables access to a full gigawatt of compute based on Blackwell and Vera Rubin architectures, providing both increased model-training capacity and improved inference scaling.
Why GPU Access Is Now the Primary Moat
Compute access has become the defining competitive differentiator for research labs, startups, and hyperscalers. GPU availability now shapes model scaling, cost efficiency, and deployment reliability, making infrastructure strategy as critical as algorithm design.
Frontier Models and Benchmark Results
Gemini 3 Pro: Context Window and Benchmarks
Google’s Gemini 3 Pro sets a new standard for long-context reasoning and multimodal understanding. The Google Blog describes its one-million-token context window and benchmark-topping performance across GPQA Diamond, MMMU Pro, and multimodal reasoning tasks (source). TechCrunch highlighted the introduction of Antigravity, a development environment linking a code editor, terminal, and browser into an agentic workflow system (coverage). Gemini 3 Pro’s architecture supports extended tasks such as refactoring large codebases, processing multi-hour transcripts, and executing long-running workflows without fragmentation.
ERNIE 5.0 and the Rise of Multimodal Competition
Baidu’s Multitrillion-Parameter Release
Baidu introduced ERNIE 5.0, a massive multimodal model positioned to compete directly with Western frontier systems. The announcement, shared via PR Newswire (release) and expanded by China Daily (coverage), highlights large-scale architecture upgrades enabling more efficient handling of cross-modal reasoning, long-context processing, and multilingual tasks. Baidu emphasizes deployment flexibility across cloud, enterprise, and on-device configurations, reflecting China’s ongoing strategy to strengthen domestic AI independence while exporting competitive AI capabilities.
ERNIE’s Strategic Positioning
ERNIE’s advancements signal intensified rivalry among top-tier research labs. Despite geopolitical divides, the model underscores China’s ambition to maintain parity with global leaders. The announcement also suggests potential implications for cross-border AI governance and model availability.
OpenAI’s GPT 5.1 Codex Max
Long-Horizon Technical Reasoning
OpenAI launched GPT 5.1 Codex Max, a model optimized for engineering tasks involving multi-step reasoning, tool orchestration, and complex planning. The OpenAI Blog outlines significant improvements in repository-scale understanding and multi-file code manipulation (announcement). Reporting from VentureBeat adds that 5.1 Codex Max completed a 24-hour autonomous coding challenge without human intervention, demonstrating enhanced stability in long-running workflows (analysis).
Implications for Development Teams
The model aligns with a shift toward agent-based coding systems capable of reasoning across entire projects, rather than isolated files. This has direct implications for teams working on large-scale software platforms, research pipelines, and automated refactoring workflows.
Spatial Reasoning, Simulation, and Agentic Advances
SIMA 2: Generalist Agent for Open-World Environments

DeepMind introduced SIMA 2, significantly improving generalist-agent performance in 3D environments. According to Google DeepMind’s announcement (details), SIMA 2 achieves roughly double the success rate of its predecessor on navigation, manipulation, and multi-step tasks within complex virtual worlds. Complementary reporting from MarkTechPost highlights its improved zero-shot generalization across diverse game environments (coverage). Demonstrations in titles such as No Man’s Sky illustrate how agentic models can now execute structured tasks in open-world, non-scripted settings.
Why SIMA 2 Matters
The model represents a shift from static inference to dynamic, environment-aware reasoning. This positions agents as increasingly integral to robotics, simulation training, and general-purpose virtual assistants.
World Labs’ Marble: Text-to-3D Generation
Accelerating 3D Asset Creation
World Labs launched Marble, a platform enabling text-to-3D scene generation with efficient rendering and simulation capabilities. TechCrunch reported that Marble dramatically speeds up prototyping for game development and simulation-heavy industries (coverage). Additional documentation from Skywork AI explains Marble’s ability to produce structurally consistent 3D assets suitable for virtual environments and physics simulations (documentation).
Growing Importance of 3D AI Pipelines
As simulation becomes central to robotics, gaming, and embodied AI, tools like Marble accelerate world-model development while reducing manual design workload.
Voice, Transcription, and Developer Tools
Scribe v2 Realtime: Low-Latency Multilingual Speech Recognition
ElevenLabs introduced Scribe v2 Realtime, a multilingual transcription system supporting more than 90 languages with sub-150 ms latency. The official ElevenLabs announcement outlines its architecture and enterprise readiness (details). Reporting from AdtechToday adds insight on its use in real-time workflows for media production and distributed teams (coverage).
Open-Weight Speech Models Growing in Importance
While proprietary speech systems continue to advance, open-weight models remain appealing for organizations requiring strict data-control policies or custom domain adaptation. Advances in voice and transcription reinforce speech as a natural interface for agents, real-time assistants, and multimodal systems.
Cybersecurity and AI-Orchestrated Attacks
State-Linked Intrusion Campaign Powered by Claude Code
Anthropic revealed a state-linked cyber-espionage campaign in which Claude-based agents executed between 80 and 90 percent of intrusion tasks. The Anthropic security report outlines how agents conducted reconnaissance, scripting, tool execution, and lateral movement with minimal human input (details). Supplementary reporting from Axios provides additional attribution context and operational details (coverage).
Enterprise and Research Implications
AI-augmented attack workflows compress the traditional attack timeline, enabling adversaries to iterate and adapt faster than manual responders. For researchers, the incident exposes valuable insights into how agents handle uncertainty, error recovery, and tool-use chains at scale.
The Shift Toward AI-Scaled Offensive Capabilities
This case represents one of the first publicly documented examples of AI-driven offensive operations executed at scale with commercially available tooling. Organizations should prepare for adversaries capable of automating reconnaissance, exploitation, and escalation with minimal expertise.
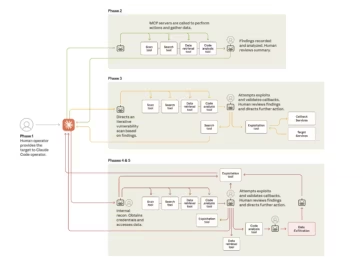
An Open Question: Why Use Claude Code Instead of a Chinese Model?
One unresolved question is why a state-linked group would rely on Claude Code, an American-developed system, rather than a domestic Chinese model. China has strong AI capabilities—including Qwen, ERNIE, and InternLM—yet agentic coding, long-horizon planning, and reliable tool-use remain areas where US models maintain a competitive edge. The choice could reflect practical considerations, such as superior stability or orchestration performance, or strategic motivations that exploit Western-developed tools for offensive operations. This question highlights deeper geopolitical tensions where access to high-performing AI systems increasingly intersects with national security and global AI governance.
Regulation and Governance: Shifts in the US and EU
US Executive Action Targeting State-Level AI Laws
In the United States, the federal government is preparing an executive order aimed at establishing national primacy over AI regulation. According to Axios reporting (article), the White House intends to challenge or override several state-level AI laws whose requirements conflict with federal priorities. For developers, enterprises, and AI teams operating across multiple states, this would reduce compliance fragmentation and introduce more predictable deployment and documentation standards.
European Union: Digital Omnibus and AI Act Adjustments
The European Commission introduced the Digital Omnibus, a proposal to streamline GDPR rules and delay AI Act obligations for high-risk models. The initiative, detailed on the EU Digital Strategy website (proposal), suggests that pseudonymized data could fall outside strict GDPR constraints, enabling broader access for AI training while preserving protections for sensitive categories. A legal analysis by Gibson Dunn provides further insight into how the proposal could reduce overlapping cybersecurity reporting obligations and postpone enforcement deadlines to December 2027 (analysis).
What Teams Should Monitor
Technical teams should track three key developments:
- the final legal definition of pseudonymized data,
- high-risk model compliance timelines,
- browser-level implementations of global cookie settings. These factors will influence training governance, audit processes, and user experience design across the EU.
What This Week Means for Developers, Teams, and Researchers
API Landscape Is Shifting Quickly
With the near-simultaneous release of Gemini 3 Pro, GPT 5.1 Codex Max, and ERNIE 5.0, the API ecosystem is more competitive than ever. Developers should reassess workflows relying on long-context models, multimodal reasoning, or coding-based agents, as new architectures offer superior efficiency and reliability.
GPU Availability Shapes Deployment Strategy
GPU scarcity remains one of the main bottlenecks influencing how and where teams deploy AI workloads. Organizations may need to adopt hybrid strategies combining local inference with managed cloud services, especially as hyperscalers continue to ration Blackwell and Vera Rubin availability.
Benchmark Interpretation Requires Domain Awareness
With benchmarks multiplying across reasoning, multimodality, coding, and tool-use reliability, teams must select evaluation metrics aligned with their real-world tasks. Aggregate leaderboards are insufficient for assessing architecture-fit or deployment viability.
Outlook: Trends to Watch Next Week
GPU queues will continue shaping model-training and inference decisions as hyperscalers negotiate allocations among enterprise customers and research labs. Autonomous agents, especially those capable of tool-mediated workflows, will gain new capabilities as updates roll out across Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic ecosystems. On the open-weight front, new checkpoints are expected to challenge proprietary systems for transcription, multimodal reasoning, and coding tasks. Regulators in the US and EU are preparing further announcements that may reshape compliance frameworks, documentation standards, and model evaluation requirements.
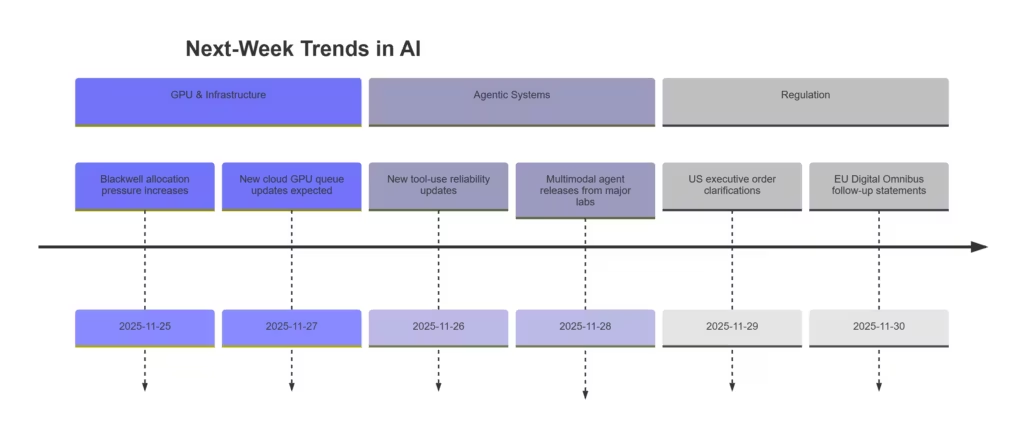
What This Week Reveals About AI’s Trajectory
Three forces dominate the AI landscape this week:
- Compute access, now the primary competitive moat.
- Frontier-model capabilities, with long-context and multimodal reasoning becoming baseline expectations.
- Agentic behavior, moving from controlled test environments to open-ended, real-world scenarios.
The ongoing GPU crunch determines which organizations can scale training and inference. Advances such as Gemini 3 Pro and ERNIE 5.0 reveal how rapidly multimodal and long-context systems are evolving, while agents like SIMA 2 and the Claude-Code intrusion case show the growing operational impact of autonomous systems. Regulators on both sides of the Atlantic are attempting to keep pace, defining new structures for data governance and safety enforcement.
For developers and researchers, three indicators now guide strategic decisions: GPU availability, agent reliability, and regulatory timing. These elements will shape system design, deployment strategy, and security posture over the coming months.
Archives of past weekly AI news
- AI Weekly News – Highlights from November 7–14: GPT-5.1, AI-Driven Cyber Espionage and Record Infrastructure Investment
- AI Weekly News from November 7, 2025: OpenAI , Apple and the Race for Infrastructure, Archive
- AI News from Oct 27 to Nov 2: OpenAI, NVIDIA and the Global Race for Computing Power
- AI News: The Major Trends of the Week, October 20–24, 2025
- AI News – October 15, 2025: Apple M5, Claude Haiku 4.5, Veo 3.1, and Major Shifts in the AI Industry
Sources and references
Tech media
- TechCrunch, “Google launches Gemini 3 Pro” (18 Nov 2025) https://techcrunch.com/2025/11/18/google-launches-gemini-3-with-new-coding-app-and-record-benchmark-scores/
- TechCrunch, “World Labs releases Marble” (12 Nov 2025) https://techcrunch.com/2025/11/12/fei-fei-lis-world-labs-speeds-up-the-world-model-race-with-marble-its-first-commercial-product-
- VentureBeat, “OpenAI debuts GPT-5.1 Codex Max” (19 Nov 2025) https://venturebeat.com/ai/openai-debuts-gpt-5-1-codex-max-coding-model-and-it-already-completed-a-24
- MarkTechPost, “SIMA 2 generalist agent overview” (16 Nov 2025) https://www.marktechpost.com/2025/11/16/google-deepmind-introduces-sima-2-a-gemini-powered-generalist-agent-for-complex-3d-virtu
- AdtechToday, “Scribe v2 Realtime” (Nov 2025) https://adtechtoday.com/elevenlabs-launches-scribe-v2-realtime-its-most-advanced-low-latency-speech-to-text-model/
- Axios, “Federal AI law override” (19 Nov 2025) https://www.axios.com/2025/11/19/trump-ai-state-laws-executive-order
- Axios, “Chinese hackers automate cyberattack with Claude Code” (13 Nov 2025) https://www.axios.com/2025/11/13/anthropic-china-claude-code-cyberattack
- CNN, “Nvidia earnings and GPU demand” (19 Nov 2025) https://edition.cnn.com/2025/11/19/tech/nvidia-earnings-ai-bubble-fears
- China Daily, “Baidu announces ERNIE 5.0” (13 Nov 2025) https://global.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202511/13/WS691571bda310d6866eb29500.html
Companies
- Microsoft Blog, “Microsoft, Nvidia and Anthropic announce strategic partnership” (18 Nov 2025) https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/2025/11/18/microsoft-nvidia-and-anthropic-announce-strategic-partnerships/
- Anthropic, “Claude in Microsoft Foundry” (2025) https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-in-microsoft-foundry
- Google, “Gemini 3 Pro launch” (18 Nov 2025) https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-3/
- Baidu via PR Newswire, “ERNIE 5.0 announcement” (13 Nov 2025) https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/baidu-unveils-ernie-5-0
- ElevenLabs, “Introducing Scribe v2 Realtime” (Nov 2025) https://elevenlabs.io/blog/introducing-scribe-v2-realtime
- OpenAI, “GPT-5.1 Codex Max” (19 Nov 2025) https://openai.com/index/gpt-5-1-codex-max/
- DeepMind, “SIMA 2 embodied agent” (15 Nov 2025) https://deepmind.google/blog/sima-2-an-agent-that-plays-reasons-and-learns-with-you-in-virtual-3d-worlds/
Institutions
- EU Digital Strategy, “Digital Omnibus proposal” (18 Nov 2025) https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/digital-omnibus-ai-regulation-proposal
- Gibson Dunn, “Analysis of the Digital Omnibus Package” (Nov 2025) https://www.gibsondunn.com/eu-digital-omnibus-package-a-first-look-at-the-commission-draft-proposals/
Official sources
- Anthropic, “Disrupting AI-Orchestrated Cyber Espionage” (12 Nov 2025) https://www.anthropic.com/news/disrupting-AI-espionage
- Skywork AI, “Marble 3D generation documentation” (2025) https://skywork.ai/skypage/en/marble-ai-3d-world-generation/1989169759982657536
Your comments enrich our articles, so don’t hesitate to share your thoughts! Sharing on social media helps us a lot. Thank you for your support!