Developer AI News : Latest Updates for Engineers
The AI ecosystem is entering a phase of rapid structural change. Models are updating faster, runtimes are fragmenting across increasingly specialized hardware, and agent frameworks are evolving from experimental prototypes into predictable, production-grade systems. With new releases of vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, ONNX, MLX, and the continued rise of graph-based orchestration tools like LangGraph, developers now face an environment where modularity, observability, and deterministic execution are no longer optional. These shifts redefine how multi-step reasoning, tool-augmented workflows, and multimodal pipelines must be designed, tested, and maintained, especially as model upgrades introduce behavioral changes that ripple across entire agent architectures. For a broader view of the latest developments across the AI landscape, explore the weekly coverage on our dedicated page.
This Week’s Highlights at a Glance
This section provides an immediate, scannable view of the most important developer-focused AI updates, structured for clarity, snippet readiness, and rapid decision-making.
| Area | Tool/Model | Version / Change | Impact for Developers |
|---|---|---|---|
| APIs & SDKs | Gemini 3 | 1M context, thinking_level, concurrent tools | Finer control over reasoning depth, lower latency, reduced multimodal token costs. |
| APIs & SDKs | Claude Opus 4.5 | Improved hybrid reasoning, stronger injection safety | More predictable agent behavior and safer handling of untrusted input. |
| APIs & SDKs | DeepSeek V3.2 | Reasoning-first architecture, improved tool-use | Better reproducibility and clearer reasoning steps for evaluation workflows. |
| Inference Runtimes | vLLM | Scheduler & multimodal stability improvements | More consistent throughput and lower jitter on long or mixed workloads. |
| Inference Runtimes | TensorRT-LLM | MoE routing & Hopper-optimized kernels | Faster, more deterministic GPU inference for latency-critical deployments. |
| Inference Runtimes | ONNX Runtime | CPU/ARM attention & operator optimizations | Higher performance for edge and hybrid deployments without GPUs. |
| Local Runtime | MLX (Apple Silicon) | Kernel & caching improvements | Faster prototyping on M-series laptops, smoother long-context inference. |
| Frameworks | LangGraph 1.0 | Durable agents, structured orchestration | More reliable multi-step agents with resumable workflows. |
| Multimodal | HunyuanVideo-1.5 | SSTA long-context video attention | Lower VRAM usage, improved temporal coherence for video generation. |
| Multimodal | FLUX.2 | Mistral 3 Small encoder, multi-image conditioning | Better prompt alignment and more controllable diffusion pipelines. |
| Infrastructure | SageMaker | Flexible inference plans | Predictable GPU capacity, fewer cold starts, more stable latency. |
| Infrastructure | NVIDIA PyTorch 25.11 | FP8 support, Volta deprecation | Higher efficiency on Hopper GPUs, mandatory planning for legacy hardware. |
| Pricing | Gemini Grounding | Shift to usage-based billing | Requires tighter monitoring of retrieval-heavy agent workloads. |
Google’s Gemini 3 introduces expanded reasoning controls and multimodal parameters, along with concurrent tool execution in a single request. According to the Gemini API changelog, developers gain more precise control over latency, accuracy, and token usage when building agentic systems or multimodal pipelines. Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 improves hybrid reasoning reliability and reduces exposure to prompt injection, as detailed in the Anthropic Transparency Hub, strengthening the model’s suitability for regulated or enterprise-grade workflows. DeepSeek V3.2 refines its reasoning-first architecture and tool-use behavior, improving reproducibility and alignment in systems that rely on structured intermediate steps.
Inference runtimes also advance quickly. vLLM introduces more stable scheduling and multimodal handling, while TensorRT-LLM deepens its GPU-level optimizations for Hopper-class hardware as documented in the TensorRT-LLM release notes. ONNX Runtime continues expanding CPU and ARM optimizations, and MLX improves local iteration workflows on Apple Silicon. LangGraph 1.0 formalizes durable agent orchestration, while multimodal frameworks such as HunyuanVideo and FLUX.2 extend video and diffusion capabilities, with technical details provided in the HunyuanVideo model card and FLUX.2 announcement. Infrastructure updates include AWS’s extension of SageMaker Flexible Plans to inference workloads, highlighted in the AWS release note, and NVIDIA’s PyTorch 25.11 container, which drops Volta support and promotes FP8 execution as described in the NVIDIA PyTorch documentation.
API and SDK Updates: What Engineers Must Know
APIs and SDKs continue evolving in ways that materially affect how developers design reasoning pipelines, manage multimodal workloads, and structure agentic systems. This section consolidates the most impactful updates, focusing on integration behavior, latency tradeoffs, and practical migration considerations for ML engineers and software developers.
Gemini 3: 1M context, reasoning controls, and multi-tool execution
Google’s Gemini 3 expands its capabilities with a 1 million token context window and the introduction of the thinking_level parameter, allowing developers to tune reasoning depth according to task complexity. As detailed in the Gemini API changelog, these controls help balance accuracy and latency in multi-step workflows and enable more predictable planning behavior in agent systems. Adjustable media resolution lowers token overhead for image and video inputs, providing finer cost management for multimodal pipelines.
Gemini 3 also supports concurrent tool execution in a single request, streamlining architectures built on Search Grounding, code execution, or document processing. This reduces pipeline fragmentation and enables tighter integration across retrieval and generation stages, improving throughput for agent-driven applications.
| Feature / Update | Description | Developer Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1M Token Context Window | Expanded long-context support across text and multimodal inputs | Enables larger documents, extended reasoning chains, unified context |
| thinking_level Parameter | Adjustable depth of reasoning and step complexity | Fine-grained control over latency vs. reasoning quality |
| Concurrent Tool Execution | Multiple tools can run within a single API call | Reduced orchestration overhead, faster multi-step agent workflows |
| Adjustable Media Resolution | Configurable image/video input granularity | Lower token consumption for multimodal pipelines |
| Improved Multimodal Handling | Better alignment between text, images, and video | More reliable output in complex multimodal tasks |
| Grounding API Pricing Change | Transition to usage-based billing | Requires call optimization, monitoring, and batching strategies |
| Enhanced Planning & Retrieval | More stable behavior in search-augmented workflows | Better performance for agentic systems using Search Grounding |
| Structured Output Improvements | More predictable schema-based responses | Easier integration into production pipelines with strict formatting |
Because Google will transition Search Grounding to usage-based billing, teams integrating heavy retrieval components must monitor call patterns to avoid unexpected cost spikes.
Claude Opus 4.5: hybrid reasoning and injection resistance improvements
Claude Opus 4.5 strengthens hybrid reasoning performance and reduces successful prompt injection attempts, enhancing safety and reliability for enterprise applications. The improvements documented in the Anthropic Transparency Hub make the model more predictable when handling untrusted input, which is essential for automated coding systems and tool-enabled agents. Updates to its multimodal capabilities also improve consistency in workflows involving structured document interpretation or image-backed reasoning.
(Click to enlarge)
Claude’s increased stability is particularly valuable in contexts where determinism, transparency, and guardrail integrity are key requirements.
DeepSeek V3.2: reasoning-first architecture and tool-use endpoints
DeepSeek V3.2 reinforces its reasoning-first design, separating internal reasoning steps from external tool execution. As described in the DeepSeek API update, this improved separation enhances debuggability and reproducibility, especially in evaluation-heavy or logic-intensive environments. The V3.2-Speciale endpoint, tuned for complex benchmark problems, has limited availability, so teams depending on its behavior should plan for timely migration.
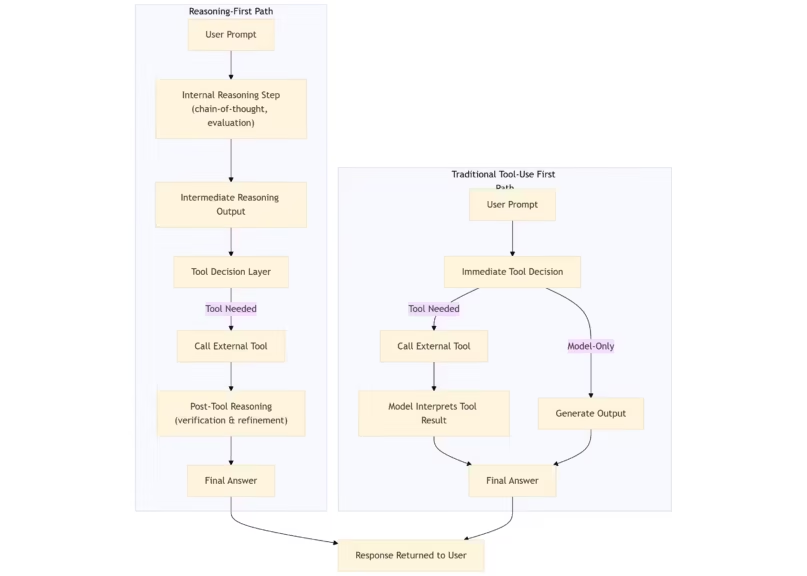
The model’s refined tool-use flow improves reliability in agent systems where deterministic tool invocation and traceability are essential.
Inference Runtimes: vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, ONNX, MLX
Inference runtimes remain one of the most strategically important layers in the modern AI stack. They dictate not only token throughput and latency, but also cost efficiency, cross-platform portability, and how reliably an application can scale across heterogeneous hardware. This week’s updates show continued divergence between flexible, general-purpose runtimes and highly optimized GPU-centric engines.
vLLM updates: scheduling, multimodal handling, and GitHub improvements
vLLM continues to evolve as a high-throughput, developer-friendly runtime. Recent updates on the vLLM GitHub repository highlight more deterministic scheduling, improved batch formation, and more robust output streaming across heterogeneous workloads. These refinements reduce jitter during long-context inference and improve stability for pipelines that interleave text and image tokens.
Developers experimenting with quantization benefit from clearer compatibility layers for NF4 and 4-bit models, easing integration with evaluation loops or production workloads that require lower VRAM footprints.
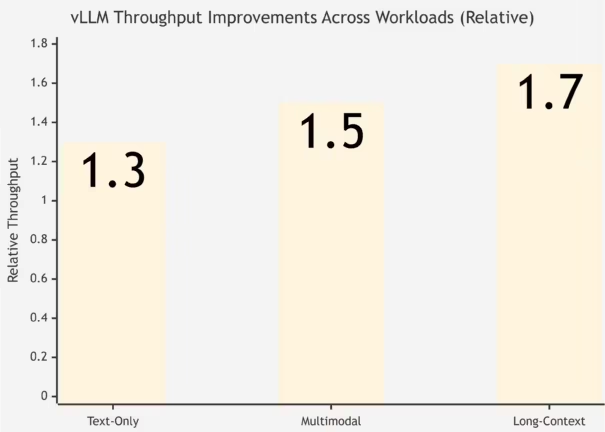
vLLM remains a strong fit for teams that require flexibility across research, prototyping, and production, without depending on hardware-specific kernels.
For readers comparing local inference stacks or evaluating how vLLM fits into a broader on-device deployment strategy, see our analysis: Ollama vs vLLM: which solution should you choose to serve local LLMs.
TensorRT-LLM: performance evolution, routing refinements, and GPU constraints
TensorRT-LLM deepens its focus on performance and latency determinism, especially for Mixture-of-Experts architectures. The latest updates described in the TensorRT-LLM release notes include routing improvements and kernel-level optimizations tuned for Hopper-generation GPUs. These changes yield measurable gains in step time and tail latency, strengthening TensorRT-LLM’s appeal for large-scale, latency-sensitive deployments.
| Model / Workload Type | Runtime | Relative Latency (lower is better) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLM (Text-Only, Short Seq) | vLLM | 1.00 | Baseline scheduler latency on comparable GPU. |
| TensorRT-LLM | 0.72 | Faster kernel execution and optimized attention on Hopper. | |
| LLM (Long-Context) | vLLM | 1.00 | Higher jitter for extended sequence lengths. |
| TensorRT-LLM | 0.68 | More consistent tail latency due to fused kernels. | |
| Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) | vLLM | 1.00 | Routing overhead not fully optimized. |
| TensorRT-LLM | 0.60 | Improved MoE routing per latest TRT-LLM updates. | |
| Multimodal Pipeline | vLLM | 1.00 | Stable but less specialized for GPU-heavy ops. |
| TensorRT-LLM | 0.75 | Gains from GPU-optimized cross-attention and batching logic. |
The tradeoff remains hardware specificity. TensorRT-LLM excels in GPU-rich environments but offers limited flexibility for hybrid or CPU-heavy deployments.
ONNX Runtime: portable optimizations for CPU and ARM
ONNX Runtime continues delivering improvements for CPU and ARM architectures, reinforcing its position as the most portable inference engine in the ecosystem. Updates highlighted in the ONNX Runtime documentation include optimized attention kernels, better operator fusion, and reduced overhead for mid-sized LLMs.
These optimizations help teams deploying models across edge devices, embedded systems, or clusters where GPU access is constrained.
ONNX remains a practical option for developers seeking predictable performance without expensive hardware dependencies.
MLX for Apple Silicon: improved kernels and prototyping efficiency
MLX continues to improve its execution path on Apple Silicon hardware. According to updates from the MLX repository, enhancements to attention kernels, memory flows, and caching behavior reduce latency for long-context inference and accelerate local prototyping.
These improvements matter for researchers and developers iterating on LLM architectures or multimodal prompts on M-series laptops.
While not intended for production-scale workloads, MLX provides a streamlined environment for lightweight experimentation and testing prior to deployment on cloud GPUs.
Framework and Tooling Releases for Developers
Frameworks and tooling continue to evolve toward more structured, reliable, and multimodal-aware development workflows. This week’s updates strengthen agent orchestration, improve video and diffusion capabilities, and reduce the friction developers face when handling long-context or high-dimensional workloads.
LangGraph 1.0: durable agents and graph-based orchestration
LangGraph 1.0 reaches general availability with a stable architecture centered on persistent state, explicit workflow control, and built-in observability. According to the LangGraph announcement, the framework introduces precise transition rules, retry logic, and human-in-the-loop checkpoints. These capabilities are essential for agent pipelines that must resume cleanly after interruptions, operate across distributed or latency-sensitive systems, or maintain consistent behavior as underlying LLMs evolve.
Also read : LangGraph: the open-source backbone of modern AI agents
For developers building multi-step reasoning systems, tool-enabled agents, or evaluation workflows, LangGraph reduces debugging complexity and increases determinism by making state transitions traceable. The consolidation of older langgraph.prebuilt modules into the newer langchain.agents namespace further simplifies maintenance and provides a clearer foundation for future deployments.
Also read : Understanding the LangChain Ecosystem: Which Solutions Fit Your AI Projects?
Diffusion and video generation updates: HunyuanVideo-1.5 and FLUX.2
HunyuanVideo-1.5 integrates Selective and Sliding Tile Attention to support long-context video generation. These mechanisms reduce memory load and improve temporal continuity across extended sequences. The model’s integration into Diffusers incorporates DeepcacheInference, which accelerates iterative video synthesis and makes it more viable for prototyping or creative production workflows. Technical details are available in the HunyuanVideo-1.5 model card.
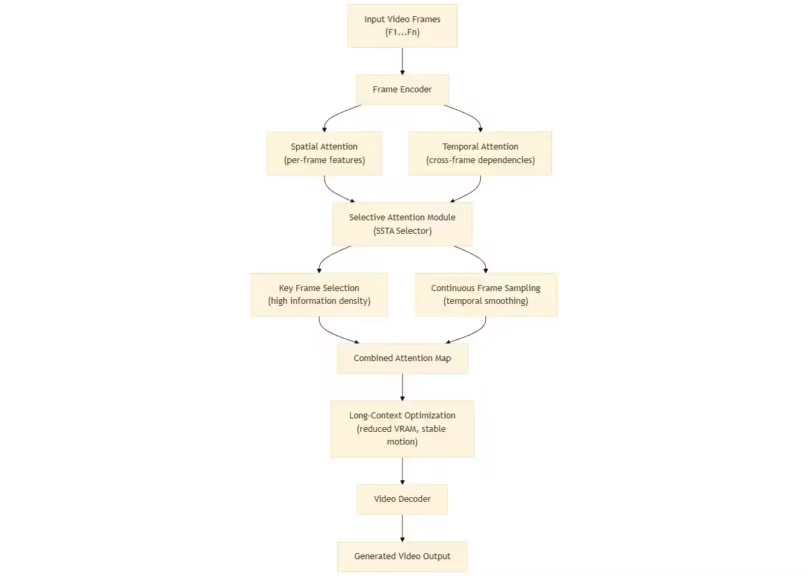
FLUX.2 introduces a larger Diffusion Transformer architecture that uses Mistral 3 Small as its text encoder, improving semantic alignment between text prompts and generated images. Multi-image conditioning allows developers to better control composition when referencing multiple assets. The FLUX.2 announcement details its quantization options, including NF4 and 4-bit variants that make it deployable on mid-tier GPUs. Flux 2 is now available in a paid Pro edition and an open-weight Dev release, with a smaller “Klein” version, essentially a compact Flux 2 Schnell, coming soon.






These updates reflect a broader industry trend toward making multimodal generation more efficient and developer-friendly, with abstractions that reduce the operational complexity of handling high-dimensional input and output.
Infrastructure, Pricing, and Deployment Constraints
Infrastructure updates and pricing changes increasingly shape how engineers deploy, scale, and optimize inference workloads. This week’s developments emphasize predictable capacity planning, hardware transitions, and new cost models for advanced API features.
SageMaker Flexible Plans for Inference
AWS now extends its Flexible Training Plans to inference endpoints, allowing developers to reserve GPU capacity with automated provisioning and deprovisioning. As described in the AWS announcement, this approach provides more predictable latency under fluctuating demand and removes the operational burden of manual endpoint scaling. It is particularly beneficial for applications requiring consistent response times during peak intervals, such as customer-facing LLM services or high-throughput agent pipelines.
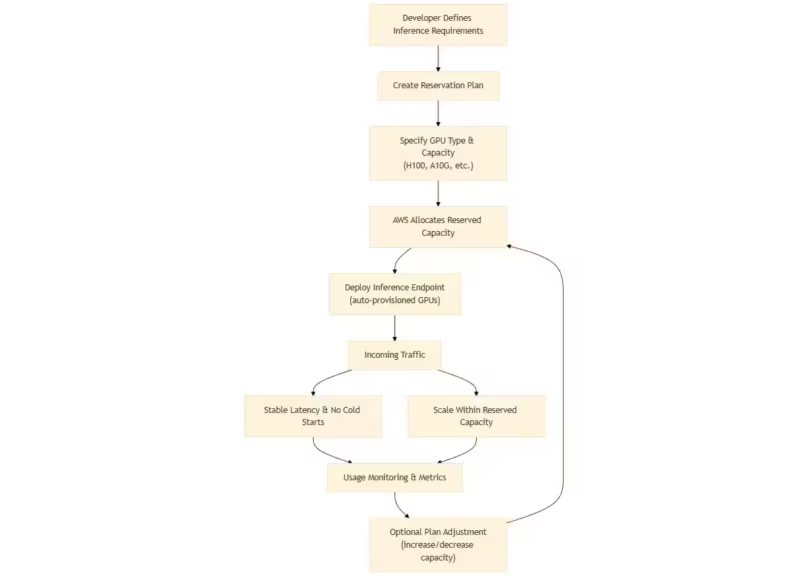
By reserving capacity, teams reduce cold-start delays and avoid resource contention during traffic bursts. This model also supports more accurate budgeting for sustained inference workloads, especially when paired with aggressive scaling codes or quantized deployments.
NVIDIA PyTorch 25.11: Volta deprecation and FP8 optimization
NVIDIA’s PyTorch 25.11 release, documented in the PyTorch container notes, finalizes the deprecation of Volta GPUs and reinforces a shift toward Hopper-class and future architectures. The inclusion of Transformer Engine features for FP8 inference allows substantial gains in throughput while lowering memory usage. Developers can adopt FP8 execution with minimal code changes, making it easier to improve performance on compatible hardware.
Teams running legacy hardware clusters must evaluate upgrade plans or migrate to cloud platforms offering newer accelerators. FP8 support will likely become standard across inference pipelines as more runtimes and models adopt lower-precision computation.
Pricing shifts in Gemini Grounding and other APIs
Google’s transition to usage-based billing for Gemini Grounding introduces new cost considerations for agent systems and retrieval-heavy workflows. The change, outlined in the Gemini API changelog, means each grounding request now has a direct budget impact. Applications that use Search Grounding extensively in planning loops or multi-tool chains must reassess call frequency and batching strategies.
This shift toward fine-grained metering reflects a broader industry trend. As models become more multimodal and tool-enabled, pricing structures are adapting to the computational cost of specialized capabilities.
GitHub Releases Watchlist
GitHub activity often reveals ecosystem shifts before they appear in formal announcements. Monitoring these repositories helps developers anticipate breaking changes, evaluate new optimization paths, and stabilize production deployments. This week’s updates highlight sustained momentum across inference engines, SDK ecosystems, and agent frameworks.
vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, ONNX Runtime, MLX
The latest commits in the vLLM repository focus on more stable scheduling, improved batch formation, and enhanced streaming consistency during long-context inference. These refinements reduce output jitter and help developers running heterogeneous workloads that mix text and image tokens.
TensorRT-LLM continues its performance-oriented trajectory. Updates in the TensorRT-LLM release notes refine routing mechanisms for Mixture-of-Experts models and optimize kernels for Hopper-generation GPUs. These changes strengthen its role in latency-critical and large-scale inference environments.
ONNX Runtime maintains steady progress toward CPU and ARM optimization. The ONNX Runtime documentation highlights improvements to attention kernel efficiency and operator fusion, reinforcing ONNX’s value for edge or hybrid-cloud deployments.
MLX advances memory handling and attention kernel efficiency on Apple Silicon, as documented in the MLX repository. These enhancements benefit researchers and developers iterating locally before deploying to more specialized GPU environments.
| Repository | Latest Tag / Update | Key Changes | Developer Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | Latest GitHub commits | Improved scheduler stability, better batch formation, enhanced streaming | More consistent throughput and reduced jitter on long-context or multimodal workloads. |
| TensorRT-LLM | Recent release notes | Optimized MoE routing, Hopper-tuned kernels | Lower latency and more deterministic GPU performance for large-scale inference. |
| ONNX Runtime | Recent documentation updates | CPU/ARM attention optimizations, improved operator fusion | Better performance on edge devices and hybrid clusters without GPUs. |
| MLX (Apple Silicon) | Latest MLX repository updates | Faster attention kernels, improved caching and memory handling | More efficient local prototyping and smoother long-sequence inference on M-series chips. |
| LangGraph | 1.0 GA release | Durable state, improved orchestration, migration from prebuilt modules | More reliable long-running agents with clearer workflow structure. |
| SAP AI SDK | Latest JS/Python release notes | Improved authentication, error handling, developer ergonomics | Easier integration and more stable SDK behavior across enterprise environments. |
| Vercel AI SDK | Beta v6 updates | Refined streaming API, better model selection, improved serverless support | Smoother integration for frontend/serverless apps using LLMs. |
Framework and SDK repos to monitor
The agent and application-layer ecosystem also sees meaningful movement. According to the LangGraph 1.0 announcement, updates refine state persistence and integration hooks that support more durable workflows. SAP’s AI SDKs receive incremental improvements in error handling, authentication consistency, and developer ergonomics, detailed in the SAP SDK release notes. Vercel’s AI SDK continues to optimize streaming behavior and improve support for frontend and serverless contexts, as outlined in its AI SDK documentation.
| Framework / SDK | Latest Update / Release Notes | Key Changes | Migration Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| LangGraph 1.0 | GA release (as announced in LangGraph 1.0 launch post) | Durable state, explicit workflow nodes, improved orchestration | Requires migration from deprecated langgraph.prebuilt modules; update agent definitions for new structure. |
| SAP AI SDK | Latest JS/Python release notes | Improved authentication flow, better error handling, consistency fixes | Verify API auth integration; update client libraries to avoid breaking changes. |
| Vercel AI SDK (v6) | v6 Beta announcement | Enhanced streaming API, improved model selection handling, better serverless integration | Review streaming implementations; update endpoints for new model-selection schema. |
| Diffusers (Hugging Face) | Recent integrations with HunyuanVideo and FLUX.2 | Support for SSTA video features and DeepcacheInference; expanded multi-image conditioning | Ensure compatibility with new scheduler interfaces; update pipelines for long-context video generation. |
| MLX (Apple Silicon) | Latest GitHub updates | Faster attention kernels, improved caching, unified memory optimizations | No breaking change expected; beneficial for local prototyping and long-context workloads. |
| LangChain (Agents) | Incremental updates aligned with LangGraph integration | Better tool-calling consistency, improved evaluation functions | Check for deprecated agent patterns; migrate to new agent execution model as recommended. |
Teams using multi-agent systems or orchestrating multiple model backends should monitor these repositories closely to avoid compatibility breaks and to incorporate new, more stable primitives as they become available.
Engineering Impact: What Developers Should Do Next
The rapid evolution of APIs, inference runtimes, and agent frameworks means engineering teams must translate weekly updates into concrete, defensible decisions. This section distills the operational priorities and migration actions that ML engineers, MLOps teams, and software developers should consider for 2025.
Optimization priorities based on stack type
Cloud GPU environments should benchmark both vLLM and TensorRT-LLM under their specific workloads. As shown in the latest TensorRT-LLM release notes, routing and kernel improvements can significantly reduce tail latency for Hopper-class GPUs, whereas vLLM provides a more flexible foundation across mixed hardware environments. Developers handling multimodal inference or agentic planning loops should also assess Gemini 3’s reasoning controls and media-resolution features described in the Gemini API changelog, which can reduce token overhead without sacrificing model quality.
For CPU or ARM-heavy deployments, ONNX Runtime’s recent optimizations documented in the ONNX Runtime guide offer meaningful improvements in throughput for mid-sized models. These updates benefit edge devices, hybrid clusters, or applications requiring predictable performance without GPUs. On Apple Silicon, MLX continues to streamline rapid prototyping workflows, making it suitable for researchers iterating locally before deploying large-scale models to cloud GPUs.
| Runtime | Cloud GPU | On-prem GPU | CPU/ARM | Local M-series |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| TensorRT-LLM | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| ONNX Runtime | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| MLX | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
Evaluating the runtime stack by environment enables more efficient resource allocation, lower latency, and clearer VRAM constraints planning.
Migration checklist for 2025
Teams should identify workloads still running on deprecated GPU families, particularly Volta, which is no longer supported in the NVIDIA PyTorch 25.11 container. Migrating to Hopper or compatible cloud offerings ensures continued access to FP8 acceleration and other kernel-level improvements.
Agent frameworks should be reviewed for compatibility with the new LangGraph 1.0 API as detailed in the LangGraph release notes, since deprecated prebuilt modules may require minor refactoring. Pricing changes for Gemini Grounding, documented in the Gemini changelog, also require new cost-monitoring strategies for retrieval-heavy workloads.
| Area | Required Action | Urgency (1–5) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPU Hardware | Migrate workloads off deprecated Volta GPUs | 1 | PyTorch 25.11 removes support; move to Hopper or cloud alternatives offering FP8. |
| Runtime Stack | Benchmark vLLM vs TensorRT-LLM for target workloads | 2 | Differences widen for MoE and long-context models; choose based on latency requirements. |
| Agent Frameworks | Update to LangGraph 1.0 and refactor deprecated modules | 2 | Replace langgraph.prebuilt components and align with new orchestration patterns. |
| API Usage (Gemini) | Adjust workflows for usage-based billing in Gemini Grounding | 1 | Retrieval-heavy agents may see cost spikes; implement batching and monitoring. |
| API Usage (Claude) | Review safety and hybrid reasoning behavior changes | 3 | Claude Opus 4.5 improves injection resistance; validate existing prompts and tool flows. |
| Multimodal Pipelines | Update Diffusers pipelines for FLUX.2 and HunyuanVideo-1.5 | 3 | Ensure compatibility with new SSTA and multi-image conditioning features. |
| Edge/CPU Deployments | Validate ONNX Runtime improvements for CPU/ARM deployment | 4 | Potential latency improvements; ensure operator compatibility during migration. |
| Local Development Setup | Update MLX for improved long-context performance | 4 | Beneficial for Apple Silicon prototyping; no breaking changes expected. |
Maintaining an up-to-date migration plan mitigates risk and ensures predictable performance as dependencies evolve.
Forward-Looking Notes for Engineers
The ecosystem continues shifting toward architectures and tooling that demand greater modularity, clearer state management, and tighter integration between model reasoning, external tools, and hardware-aware runtimes. Updates across vLLM, TensorRT-LLM, ONNX, and MLX demonstrate how inference engines are becoming increasingly specialized, with each runtime optimizing for a different combination of performance, portability, and hardware constraints. Developers adopting multi-runtime strategies will need more systematic benchmarking practices to ensure predictable latency and throughput across production environments.
Agent frameworks like LangGraph are formalizing execution patterns that were previously ad hoc, introducing persistent state, explicit recovery paths, structured evaluation loops, and built-in observability. These advances allow long-running or multi-step reasoning pipelines to behave more predictably and make it possible to detect behavioral drifts when upgrading to new LLM versions. This level of traceability is increasingly critical for workflows that integrate external tools, retrieval components, or human-in-the-loop steps.
Meanwhile, multimodal tooling is evolving quickly, with models such as HunyuanVideo-1.5 and FLUX.2 introducing more memory-efficient attention mechanisms and richer conditioning strategies that reduce the barrier to running video or multi-image pipelines.
Developers can expect the pattern to continue: faster iteration cycles, more fragmented hardware targets, deeper integration between agents and retrieval systems, and increasingly granular pricing models for advanced API features.
The Broader Outlook
The latest updates across APIs, inference runtimes, tooling, and infrastructure indicate a maturing landscape where developer experience and operational efficiency matter as much as model capabilities. Teams that benchmark runtimes regularly, track GPU deprecations, and adapt to evolving pricing structures will be better positioned to manage performance and costs in 2025. As model versions evolve more rapidly, observability becomes essential for detecting behavioral shifts, validating agent pipelines, and ensuring that reasoning workflows remain stable across upgrades. Together with advances in reasoning controls, agent orchestration, and multimodal efficiency, these improvements point toward a future where AI systems are more transparent, modular, and aligned with real-world engineering constraints.
Also read : Understanding Google TPU Trillium: How Google’s AI Accelerator Works
Sources and references
Companies
According to the Gemini API changelog, Gemini 3 expands reasoning controls, multimodal options, and tool execution. Anthropic details Claude Opus 4.5 improvements in the Anthropic Transparency Hub. DeepSeek outlines its reasoning-first architecture in the DeepSeek API update. AWS introduces inference capacity reservations in the SageMaker Flexible Plans announcement. NVIDIA documents FP8 acceleration and hardware changes in the PyTorch 25.11 release notes.
Institutions
Hugging Face provides implementation details for HunyuanVideo-1.5 and FLUX.2 in their respective model cards and blog posts:
Apple documents MLX performance changes in the MLX repository.
Official sources
ONNX Runtime CPU and ARM optimizations are detailed in the ONNX Runtime documentation. TensorRT-LLM updates are tracked in the official release notes. LangGraph 1.0 migration details are available in the LangGraph announcement.
Your comments enrich our articles, so don’t hesitate to share your thoughts! Sharing on social media helps us a lot. Thank you for your support!