Practical guide: organize AI prompts with Notion (accessible solution)

Do you juggle daily with ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini, and your collection of prompts looks more like a junk drawer? You are not alone. Between instructions scribbled in random notes, prompts saved in Slack messages, and others buried in your chat history, you can spend a lot of time searching for that template that worked so well last week.
If you are looking for a solution to organize your AI prompts that is powerful yet accessible without coding skills, Notion may be your best ally. This all-in-one platform, already used by millions to manage projects and knowledge, turns out to be particularly suited for simple and effective prompt library management.
In this practical guide, we will build together, step by step, a complete system to organize AI prompts with Notion. Whether you are a freelancer, content creator, marketer, or project manager, you will learn how to transform Notion into a true command center for your AI prompt templates. The best part: everything can be done with the free plan. Before going further, check out the full guide: Organize AI prompts: complete solutions guide 2025
Why use Notion to organize AI prompts?
An accessible solution for every profile
Unlike technical tools that require Git knowledge or coding skills, Notion can be mastered in a few clicks. Its intuitive interface allows you to create sophisticated databases without writing a single line of code. You build your AI prompt library like assembling Lego bricks: drag-and-drop modular blocks that fit together naturally.
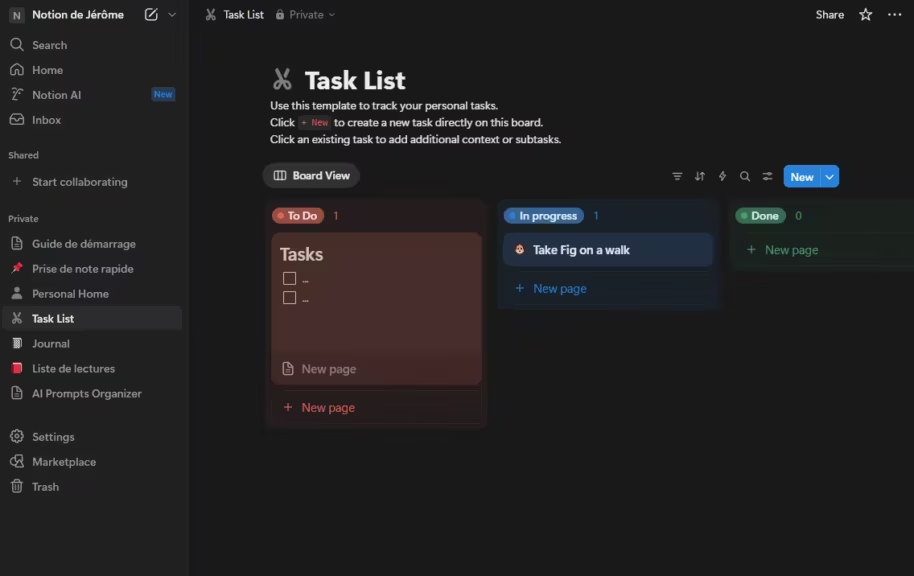
This accessibility and ease of use make it ideal for freelancers or small teams. Notion also provides advanced features (relational databases, formulas, automations) that meet the needs of professionals while remaining understandable for beginners.
A generous free plan to get started
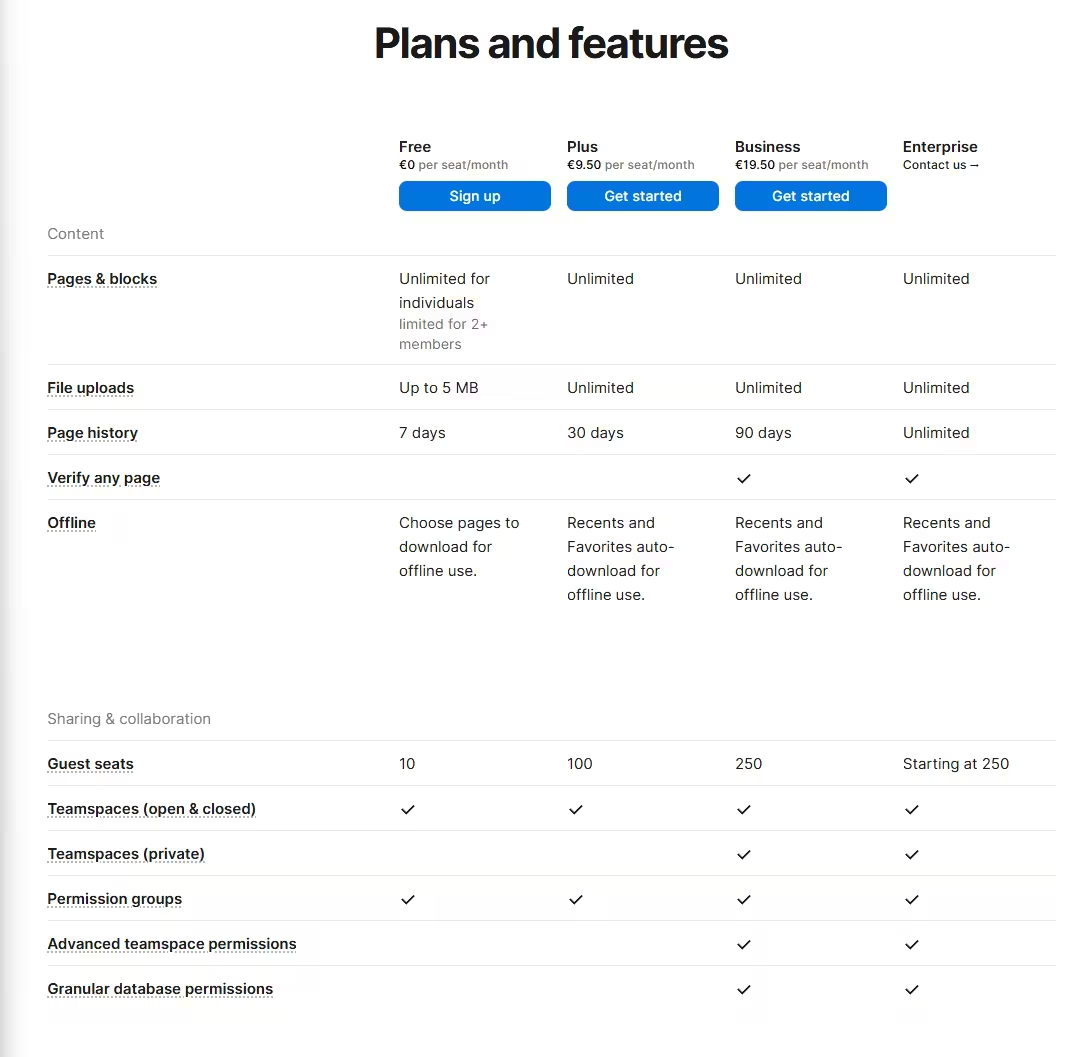
According to Notion’s pricing page, the free plan offers unlimited pages and blocks for solo users, which is more than enough to manage a personal AI prompt library. Even if you work with a team, you have 1000 shared blocks and can invite up to 10 collaborators, which is plenty to get serious without spending a dime.
The only limitations are the 5 MB file upload cap and the 7-day version history, but these do not really impact AI prompt management in Notion which relies mainly on text.
Built-in flexibility and collaboration
Notion stands out for its versatility. In the same space, you can manage your AI prompt library, project documentation, brainstorming notes, and dashboards. This unified approach avoids spreading your work across multiple tools.
Collaboration happens in real time: several members can view, edit, and improve your prompt database simultaneously. Integrated comments make it easy to discuss a specific template. Unlike a simple Google Doc, Notion structures information in a way that is searchable with tags, filters, and multiple views.
Automatic multi-device synchronization
Whether you are working on a Mac at the office, a PC at home, or your iPad on the go, your AI prompts in Notion remain synced automatically. Add a new template on mobile and it instantly appears on desktop. This constant accessibility makes your AI prompt library truly portable.
Synchronization in Notion can be slowed down by a weak or unstable internet connection. Since the app is entirely cloud-based, it depends on a stable network to load and save data properly. Lag and temporary freezes are common with large pages, complex databases, or media-heavy content. Some users also experience sync anxiety, fearing that their changes are not saved across devices (Super.so, Unleash.so, Reddit).
To limit these issues, it is recommended to:
- ensure a stable internet connection or switch networks if the signal is weak
- log out and back into Notion to refresh the session
- clear the app cache
- reduce page complexity by limiting heavy images and oversized databases
- favor the desktop version, often faster than the web or mobile app (Notion Help)
If the problem persists, contacting Notion support remains the best option to identify specific causes of slowness or desync.
Build a database of AI prompts in Notion
Step 1: Create your dedicated prompts page
Start by laying the foundation. In your Notion workspace, create a new page and name it something like “🤖 AI Prompts Library” or “Artificial Intelligence Templates”. Add an icon and cover image that you like, as visuals make the tool more pleasant to use daily.
In this page, add a Database – Table view block. This table will be the core of your AI prompt organization system in Notion. Give it a clear title such as “My AI Prompts” and set up the essential columns.
Step 2: Configure the basic properties
Here is the recommended column setup for efficient AI prompt management in Notion:
Prompt name (default text) The title of each entry. Use a clear naming convention, e.g. “SEO Blog Article”, “Sales Follow-up Email”, “Customer Sentiment Analysis”. This column is created by default as “Name” in Notion.
Category (Select property) Organize your prompts by main use case:
- Content generation
- Data extraction
- Classification / Sorting
- Analysis and summarization
- Translation
- Code and technical
- Conversation / Support
This thematic categorization makes it easy to filter your library by need.
Tags (Multi-select property) Add more granular labels: marketing, sales, blog, email, SEO, creative, formal, technical, short, long. Tags allow multidimensional navigation.
AI model (Multi-select property) Indicate which models the prompt has been tested on: GPT-4, Claude, Gemini, Mistral. This avoids wasting time testing prompts on incompatible models.
Complexity (Select property) Level of sophistication: Simple, Intermediate, Advanced. Useful when you need a beginner-friendly prompt or an expert template.
Status (Select property) Validation workflow: Draft, To test, Validated, Archived. Crucial for teams to manage prompt lifecycles.
Variables (Text property) List the variables used in the prompt: {{client_name}}, {{topic}}, {{tone}}, etc. Serves as a quick reference.
Creation date (Created time property) Automatically filled by Notion. Helps track evolution and identify recent prompts.
Last edited (Last edited time property) Also auto-filled. Useful to spot active versus unused templates.
Step 3: Fill in the prompt content
Click the first row to open the full prompt page. This is where you store each template’s details.
Structure each prompt entry as follows:
Section 1: Goal Explain in a few sentences the purpose and context. Example: “This prompt generates SEO-optimized e-commerce product descriptions with a persuasive tone and call-to-action.”
Section 2: The prompt itself Use a Code block (choose “Plain Text”) to preserve formatting. Example:
Write a product description for {{product_name}}.
Context:
- Category: {{category}}
- Key features: {{features}}
- Target audience: {{audience}}
Tone: {{tone}} (e.g. professional, casual, luxury)
Length: {{length}} words
The description must include:
1. Captivating hook
2. Key customer benefits
3. Technical features if relevant
4. Call-to-action
Section 3: Variables and examples List each variable with:
- Its exact name: {{product_name}}
- Expected content: text, list, number
- Example: “ErgoMax 3000 ergonomic office chair”
Section 4: Sample results Include one or two outputs generated with real variables. This helps visualize results and serves as a quality reference.
Section 5: Notes and optimizations Add your observations: works better with temperature 0.7, avoid overly long lists, track previous versions.
This comprehensive documentation turns each prompt into a reusable, shareable asset.
Step 4: Create custom views
Notion allows you to build multiple views of the same database. Use this feature to create perspectives adapted to different use cases:
View by category Set up a table grouped by the “Category” property. This gives you a quick overview of all prompts for content generation, extraction, etc.
Gallery view for visual navigation Switch your database to gallery mode with illustrated cards. Great for browsing templates visually. Add emoji icons in titles to make identification faster (✍️ for writing, 📊 for analysis).
Favorites view Add a Checkbox property “⭐ Favorite” and create a filtered view to show only these. Your most used AI prompts stay one click away.
View by AI model Filter prompts according to the model you are using. If you work with Claude today, display only Claude-compatible prompts.
Add variables and automation with Notion Buttons
Understanding variables in Notion
Unlike specialized tools, Notion does not have a native templating engine that substitutes variables automatically. You cannot “execute” a prompt with automatic {{variable}} replacement. However, you can design semi-automated workflows with Notion Buttons.
According to Matthias Frank, Notion Buttons let you generate pre-filled pages from templates, creating a form of elegant manual automation.
Create a prompt generation button
Insert a “Button” block in your page. Configure it to create a new page from a prompt template:
Step 1: Name the button Example: “📝 Use this prompt”
Step 2: Define the action Choose “Add a page to…” and select a target database (you might create one called “Prompts in progress”).
Step 3: Configure the template In the button options, activate “Edit template” and define the structure of the new page. Include:
- The full prompt
- Sections to fill in variables
- Space to paste the result
Template example:
## Prompt
[Prompt appears here automatically]
## To fill in before use
**{{product_name}}**: [Your input]
**{{category}}**: [Your input]
**{{features}}**: [Your input]
**{{audience}}**: [Your input]
**{{tone}}**: [Your input]
**{{length}}**: [Your input]
## Finalized prompt
[Copy the completed prompt here]
## Result
[Paste the AI output here]
Clicking the button instantly creates a page with this structure. You fill in the variables, finalize the prompt, and copy it into ChatGPT or Claude.
Using button properties for customization
Notion Buttons can include dynamic variables based on page properties. This enables more advanced workflows.
For instance, you can create a button that:
- Automatically retrieves properties like category or tags
- Pre-fills a new page with this data
- Lets you complete only the context-specific variables
This hybrid approach automates repetitive tasks while keeping flexibility.
Free plan vs paid plan limitations
Notion Buttons and variables are available on all plans, including the free one. However, advanced actions are reserved for paid plans.
On the free plan, you can create buttons, add variables, and reuse them in actions. But integrations like email sending, webhooks, or Slack notifications require a paid plan (Notion Help, Notion Pricing).
Database automations (automatically creating or updating entries) are also limited to paid subscriptions (Notion Help, Automations).
In short, variable definition in buttons is open to everyone, but complex automations and external integrations require a paid plan.
Create a quick duplication workflow
For an even simpler setup, add a “Duplicate for use” button that clones a prompt page into a section like “In progress”. You can then edit this copy, replace the {{variables}} manually, and copy the final prompt.
This method, while manual, is still fast and efficient, and preserves the original template intact.
Automation limitations in Notion
Let’s be clear: Notion is not designed as an AI automation tool. You cannot:
- Run prompts directly via an AI API
- Chain multiple prompts automatically
- Substitute variables via scripts
- Compare versions automatically
Notion excels at organizing, documenting, and preparing AI prompts, but execution remains manual. For advanced automation, consider technical tools covered in our guides on Obsidian and VS Code.
Limitations of Notion for advanced prompt engineering
No real version control
Notion offers a basic edit history (7 days on free plan, unlimited on paid) but it is not a true versioning system like Git. You can view and restore old versions but:
- No side-by-side comparisons
- No branching for variations
- No merging changes
- Only linear history
If you need rigorous versioning, Notion falls short compared to tools like PromptHub which integrates Git-style versioning.
No execution or automated testing
Unlike platforms such as PromptLayer or frameworks like LangChain, Notion does not connect to AI APIs. You cannot:
- Run prompts directly
- Compare multiple versions automatically (A/B testing)
- Track metrics (tokens, response time)
- Log usage and results
These must be managed manually or with a complementary tool.
Free plan collaboration limits
With a cap of 1000 shared blocks on the free plan (Super.so), active teams may quickly hit this limit. Each prompt page counts as several blocks (title, properties, content).
For team-wide libraries, upgrading to a paid plan ($8–10/user/month) may be necessary. Alternatively, open source tools like OpenPrompt can offer more flexibility for free.
Performance with large libraries
Notion slows down noticeably with hundreds of detailed entries. Loading times increase, searches lag. If you plan to manage 500+ AI prompts, expect performance issues.
Practical use cases: organizing prompts by theme
Example 1: Marketing and content library
Pauline, a freelance digital marketer, structured her Notion AI prompt library into five main categories:
Blog posts: 15 prompts for listicles, full guides, news, and opinion pieces Social media: 12 prompts for LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram with different objectives (engagement, promotion, thought leadership) Email marketing: 8 prompts for newsletters, welcome sequences, sales follow-ups Product pages: 5 templates for different product types and markets Ads: 6 prompts for Facebook, Google, LinkedIn ads
Each includes tone variations (B2B formal, B2C casual, luxury premium) using the {{tone}} variable. Pauline estimates saving 3–4 hours weekly since systematizing prompts in Notion instead of starting from scratch.
Example 2: Customer support and analysis
Thomas’ support team (SaaS startup, 8 people) uses Notion to centralize 25 AI prompts dedicated to customer service:
Feedback analysis: sentiment extraction, bug detection, request categorization Canned replies: templates for FAQs, common issues, escalation to tech team Summaries and reports: condense long conversations, highlight action points
Each team member can view, use, and suggest improvements. A validation workflow with the “Status” property (Proposal → Test → Validated) ensures quality.
Example 3: Academic research and analysis
Marie, a PhD student, built a Notion AI prompt library for research tasks:
Article summaries: structured reviews, methodology extraction, identifying limitations Data analysis: interpreting statistics, generating hypotheses, suggesting additional analysis Academic writing: abstract structuring, rewriting for clarity, English–French translation
She uses tags extensively (neuroscience, quantitative methods, literature review) and filtered views to navigate. The “AI model” property is critical since some prompts work better with GPT-4 while others perform better on Claude for longer analyses.
Conclusion: Notion as an accessible solution to get started
Organizing AI prompts with Notion is an excellent starting point for structuring prompt engineering without technical overhead. With an intuitive interface, a generous free plan, smooth collaboration, and strong flexibility, Notion checks many boxes for effective and accessible AI prompt management.
Of course, Notion has limits: no true Git versioning, no advanced automation, and manual execution of prompts. But for most users — freelancers, small teams, non-technical professionals — these trade-offs are acceptable compared to the ease of use. Plus, Notion allows full data export if you later move to another solution.
The Notion approach for AI prompt management shines when you want to:
- Start quickly with no steep learning curve
- Centralize and document a personal prompt library
- Collaborate easily in a small team (<10)
- Combine prompt management with project docs and notes
If you want to go further with AI template organization, including:
- Local storage and full privacy
- Automated variables and scripts
- Strict version control with Git
- Advanced prompt chaining workflows
Then explore our guides on more technical solutions:
- Organize AI prompts with Obsidian and Templater for a local and extensible approach
- Organize AI prompts with VS Code for a developer-oriented workflow
And if you are still undecided, check out our comparison of AI prompt management tools to choose based on your profile and needs.
For now, start simple: create your first Notion database, add five prompts, and experiment. You will quickly see the benefits of a well-structured AI prompt library on your daily productivity with artificial intelligence.
Your comments enrich our articles, so don’t hesitate to share your thoughts! Sharing on social media helps us a lot. Thank you for your support!